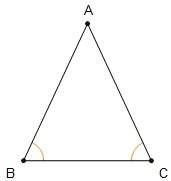
Consider the diagram and proof by contradiction.
given: △abc with ∠b ≅ ∠c
prove: ab ≅...

Mathematics, 22.09.2019 12:00 neazisa
Consider the diagram and proof by contradiction.
given: △abc with ∠b ≅ ∠c
prove: ab ≅ ac
it is given that ∠b ≅ ∠c. assume ab and ac are not congruent. if ab > ac, then m∠c > m∠b by if ac > ab, then m∠b > m∠c for the same reason. however, using the given statement and the definition of congruency, we know that m∠b = m∠c. therefore, ab = ac and ab ≅ ac.
what is the missing reason in the proof?
converse of the triangle parts relationship theorem
substitution
definition of congruency
converse of the isosceles triangle theorem

Answers: 2


Another question on Mathematics


Mathematics, 21.06.2019 14:00
Which solid has two triangular bases and three lateral faces, each in the shape of a rectangle? triangular prism triangular pyramid rectangular prism rectangular pyramid
Answers: 3

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 15:10
Fractions can be added and subtracted only if they're fractions. a. like b. proper c. improper d. unlike
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 16:00
Use set builder notation to represent the following set: { -3, -2, -1, 0}
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
Questions

English, 21.07.2020 17:01


Mathematics, 21.07.2020 17:01



Mathematics, 21.07.2020 17:01

Mathematics, 21.07.2020 17:01






Computers and Technology, 21.07.2020 17:01

Mathematics, 21.07.2020 17:01

Mathematics, 21.07.2020 17:01

Computers and Technology, 21.07.2020 17:01






