
Biology, 07.10.2019 10:30 elissiashontelbrown
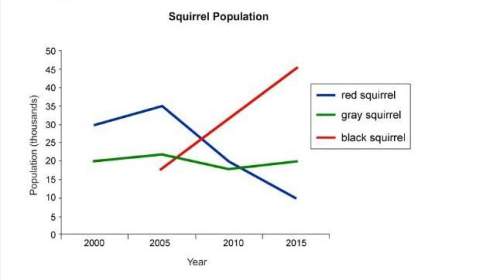
Study the population growth curve of three species of squirrels on an island. red squirrels and gray squirrels have been the native species on the island for the past 1,000 years. the black squirrel is an invasive species. invasive species aren’t native to the ecosystem. they move into an ecosystem because of natural changes or human intervention. in 2005, black squirrels entered this island. red squirrels and black squirrels have identical food requirements, but gray squirrels eat different kinds of food. what’s the plausible reason for the population change?

a.
the red squirrel has no predators, and the black squirrel has many predators.
b.
the gray squirrel competes with the black squirrel for food.
c.
the black squirrel has no predators, and the red squirrel faces higher competition for resources.
d.
the black squirrel has many predators and faces tougher competition for resources.

Answers: 3


Another question on Biology

Biology, 21.06.2019 19:00
2. in dragons, a gene on chromosome 1 codes for wing color and a gene on chromosome 2 codes for body color. draw out the stages of meiosis for these two chromosomes from a dragon that is heterozygous for both traits. define your alleles. what are all the possible allele combinations of the gametes produced?
Answers: 1

Biology, 22.06.2019 03:00
20 points and brainlist 1. london has suffered from terrible air pollution for at least seven centuries. why is the city so prone to its famous “london fog? ” what did london do to get rid of its air pollution? 2. why does air pollution cause problems in developing nations more than in developed ones?
Answers: 2

Biology, 22.06.2019 04:00
Will mark brainliest i only need the ! 1.use ten beads and a centromere of one color to construct the long chromosome. use ten beads and a centromere of a second color to construct the second chromosome in the long pair. make a drawing of the chromosomes in the space below. 2. for the second pair of chromosomes, use only five beads. 3. now model the replication of the chromosomes. make a drawing of your model in the space below. part b: meiosis i during meiosis i, the cell divides into two diploid daughter cells. 4. pair up the chromosomes to form tetrads. use the longer tetrad to model crossing-over. make a drawing of the tetrads in the space below. 5. line up the tetrads across the center of your “cell.” then model what happens to the chromosomes during anaphase i. 6. divide the cell into two daughter cells. use the space below to make a drawing of the result. part c: meiosis ii during meiosis ii, the daughter cells divide again. 7. line up the chromosomes at the center of the first cell, one above the other. separate the chromatids in each chromosome and move them to opposite sides of the cell. 8. repeat step 7 for the second cell. 9. divide each cell into two daughter cells. use the space below to make a drawing of the four haploid cells
Answers: 1

Biology, 22.06.2019 08:00
What are the student's observations and inferences before he starts his investigation?
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
Study the population growth curve of three species of squirrels on an island. red squirrels and gray...
Questions

Mathematics, 24.09.2019 03:30

Mathematics, 24.09.2019 03:30



Health, 24.09.2019 03:30


Mathematics, 24.09.2019 03:30

Mathematics, 24.09.2019 03:30

Mathematics, 24.09.2019 03:30

Mathematics, 24.09.2019 03:30

History, 24.09.2019 03:30



Mathematics, 24.09.2019 03:30

Mathematics, 24.09.2019 03:30







