
Biology, 19.04.2021 04:10 gabbypittman20
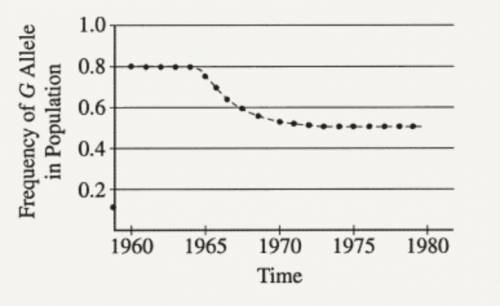
A moth's color is controlled by two alleles, G and g, at a single locus. G (gray) is dominant to g (white). A large population of moths was studied, and the frequency of the G allele in the population over time was documented, as shown in the figure below. In 1980 a random sample of 2,000 pupae was collected and moths were allowed to emerge. Assuming that the population was in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium for the G locus, what percentage of the gray moths that emerged in 1980 was heterozygous? (The Answer is 67%, can you please explain why it's 67%? thank you!!)

Answers: 3


Another question on Biology

Biology, 22.06.2019 00:30
Building glycogen from glucose molecules is an example of what
Answers: 2

Biology, 22.06.2019 01:00
Why reason best illustrates why hershey and chase chose to use viruses in their experiment?
Answers: 2

Biology, 22.06.2019 03:30
Students in biology are studying the macromolecules of life. they used a calorimeter to determine the calories in various types of food. once the lab was completed, the students ate the left over food samples. monica commented that in just 6 or 7 "chews" of the saltine, it was gone; nothing but a sticky paste in her mouth. elaborate on what happened chemically while chewing the saltine. include the macromolecules present.
Answers: 1

Biology, 22.06.2019 05:00
How will you manage your time to accomplish the necessary tasks both on the job and at home?
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
A moth's color is controlled by two alleles, G and g, at a single locus. G (gray) is dominant to g (...
Questions

Mathematics, 29.04.2021 09:10

English, 29.04.2021 09:10



English, 29.04.2021 09:10


Mathematics, 29.04.2021 09:10

Biology, 29.04.2021 09:10


Mathematics, 29.04.2021 09:10


Biology, 29.04.2021 09:10



English, 29.04.2021 09:10

Mathematics, 29.04.2021 09:10







