Business, 10.04.2020 19:25 alexisgilford
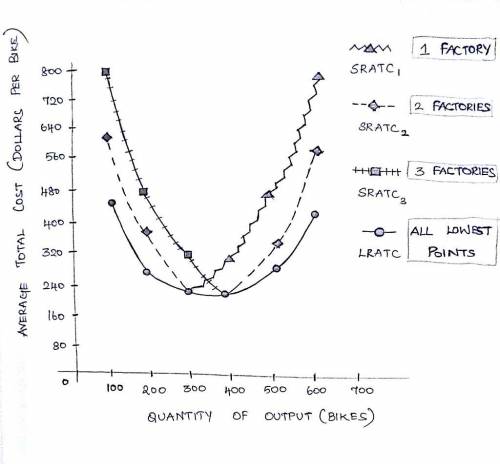
Costs in the short run versus in the long run Ike's Bikes is a major manufacturer of bicycles. Currently, the company produces bikes using only one factory. However, it is considering expanding production to two or even three factories. The following table shows the company's short-run average total cost (SRATC) each month for various levels of production if it uses one, two, or three factories. (Note: Q equals the total quantity of bikes produced by all factories.) Number of Factories Average Total Cost (Dollars per bike) Q = 100 Q = 200 Q = 300 Q = 400 Q = 500 Q = 600 1 440 280 240 320 480 800 2 620 380 240 240 380 620 3 800 480 320 240 280 440 Suppose Ike's Bikes is currently producing 600 bikes per month in its only factory. Its short-run average total cost isper bike. Suppose Ike's Bikes is expecting to produce 600 bikes per month for several years. In this case, in the long run, it would choose to produce bikes using . On the following graph, plot the three SRATC curves for Ike's Bikes from the previous table. Specifically, use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot its SRATC if it operates one factory ( ); use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot its short-run average total cost if it operates two factories ( ); and use the orange points (square symbol) to plot its SRATC if it operates three factories ( ). Finally, plot the long-run average total cost (LRATC) for Ike's Bikes using the blue points (circle symbol). Note: Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically.

Answers: 1


Another question on Business

Business, 21.06.2019 15:30
Suppose that each country completely specializes in the production of the good in which it has a comparative advantage, producing only that good. in this case, the country that produces jeans will produce 32 million pairs per month, and the country that produces corn will produce 32 million bushels per month.
Answers: 1

Business, 21.06.2019 21:30
Balance sheet baggett company's balance sheet accounts and amounts as of december 31, 2016, are shown in random order as follows: account debit (credit) account debit (credit) income taxes payable $(3,800) additional paid-in capital on preferred prepaid items 1,800 stock $(7,900) additional paid-in capital on common stock (9,300) allowance for doubtful accounts (1,600) land 12,200 bonds payable (due 2020) (23,000) notes payable (due 2019) (6,000) buildings 57,400 notes receivable (due 2018) 16,400 sinking fund to retire bonds payable 5,000 accounts receivable 12,600 advances from customers (long-term) (2,600) premium on bonds payable (1,400) cash 4,300 accounts payable (13,100) accumulated depreciation: equipment (9,700) inventory 7,400 retained earnings (18,300) accumulated depreciation: buildings (21,000) preferred stock, $100 par (18,600) patents (net) 4,600 wages payable (1,400) equipment 28,700 common stock, $10 par (12,700) required: 1. prepare a december 31, 2016 balance sheet for the baggett. baggett company balance sheet december 31, 2016 assets current assets: $ $ $ long-term investments: $ property, plant, and equipment: $ $ $ intangible assets: liabilities current liabilities: $ $ long-term liabilities: $ $ other liabilities: shareholders' equity contributed capital: $ $ $ $ 2. compute the debt-to-assets ratio. round to one decimal place. do not enter a percent sign (%) as part of your answer. %
Answers: 1

Business, 22.06.2019 04:10
Oakmont company has an opportunity to manufacture and sell a new product for a four-year period. the company’s discount rate is 18%. after careful study, oakmont estimated the following costs and revenues for the new product: cost of equipment needed $ 230,000 working capital needed $ 84,000 overhaul of the equipment in year two $ 9,000 salvage value of the equipment in four years $ 12,000 annual revenues and costs: sales revenues $ 400,000 variable expenses $ 195,000 fixed out-of-pocket operating costs $ 85,000 when the project concludes in four years the working capital will be released for investment elsewhere within the company. click here to view exhibit 12b-1 and exhibit 12b-2, to determine the appropriate discount factor(s) using tables.
Answers: 2

Business, 22.06.2019 21:10
You are the manager of a large crude-oil refinery. as part of the refining process, a certain heat exchanger (operated at high temperatures and with abrasive material flowing through it) must be replaced every year. the replacement and downtime cost in the first year is $165 comma 000. this cost is expected to increase due to inflation at a rate of 7% per year for six years (i.e. until the eoy 7), at which time this particular heat exchanger will no longer be needed. if the company's cost of capital is 15% per year, how much could you afford to spend for a higher quality heat exchanger so that these annual replacement and downtime costs could be eliminated?
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
Costs in the short run versus in the long run Ike's Bikes is a major manufacturer of bicycles. Curre...
Questions

Mathematics, 15.12.2020 22:20

Spanish, 15.12.2020 22:20


Business, 15.12.2020 22:20


History, 15.12.2020 22:20


Mathematics, 15.12.2020 22:20

Social Studies, 15.12.2020 22:20

Mathematics, 15.12.2020 22:20


Mathematics, 15.12.2020 22:20

Spanish, 15.12.2020 22:20

Mathematics, 15.12.2020 22:20

Arts, 15.12.2020 22:20

Mathematics, 15.12.2020 22:20



History, 15.12.2020 22:20

Mathematics, 15.12.2020 22:20