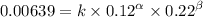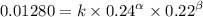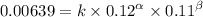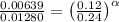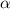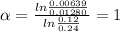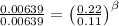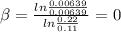Chemistry, 11.09.2019 03:10 taminazaka1
Reaction rates
part a
for the arbitrary reaction,
a + b ? c + d
the following initial rates were measured given the initial concentrations of a and b. determine the rate order for both a and b.
[a]o [b]o initial rate (m/s)
0.12 0.22 0.00639
0.24 0.22 0.0128
0.12 0.11 0.00639
part b
-0th order in a and 1st order in b
-2nd order in a and 0th order in b
-1st order in a and 1st order in b
-1st order in a and 0th order in b
the following arbitrary reaction is exothermic:
a + b ? c + d
predict what will happen to the rate of the reaction if the temperature is increased.
-the reaction rate will decrease.
-equilibrium is shifted to the left.
-the reaction rate increases.
-there will be no change in rate.

Answers: 2


Another question on Chemistry

Chemistry, 21.06.2019 19:00
Identify which properties could correspond to solids, plasmas, or both. maintain a unique shape. collide infrequently with other particles. have very high velocities. conduct electricity. protons. have a low temperature. has long-range order.
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 21.06.2019 23:30
Problem #3 (ch. 1, problem 15)the ideal gas law provides one way to estimate the pressure exerted by a gas on a container. the law isí‘ťí‘ť=푛푛푛푛푛푛푉푉more accurate estimates can be made with the van der waals equationí‘ťí‘ť=푛푛푛푛푛푛푉푉â’푛푛푟푟â’푞푞푛푛2푉푉2where the term nb is a correction for the volume of the molecules and the term an2/v2is a correction for molecular attractions. the values of a and b depend on the type of gas. the gas constant is r, the absolutetemperature is t, the gas volume is v, and the number of moles of gas molecules is indicated by n. if n = 1 mol of an ideal gas were confined to a volume of v = 22.41 l at a temperature of 0â°c (273.2k), it would exert a pressure of 1 atm. in these units, r = 0.0826.for chlorine gas (cl2), a = 6.49 and b = 0.0562. compare the pressure estimates given by the ideal gas law and the van der waals equation for 1 mol of cl2 in 22.41 l at 273.2 k. what is the main cause of the difference in the two pressure estimates, the molecular volume or the molecular attractions?
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 10:30
Consider the following reactions. (note: (s) = solid, (l) = liquid, and (g) = gas.) mg(s) + ½o2(g) → mgo(s) + 146 kcal/mole h2(g) + ½o2(g) → h2o(g), δh = -57.82 kcal/mole what type of reaction is represented by the previous two examples?
Answers: 3

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 12:30
The bond energy for the van der waals bond between two helium atoms is 7.9×10−4ev. assuming that the average kinetic energy of a helium atom is (3/2)kbt, at what temperature is the average kinetic energy equal to the bond energy between two helium atoms
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
Reaction rates
part a
for the arbitrary reaction,
a + b ? c + d
the fol...
part a
for the arbitrary reaction,
a + b ? c + d
the fol...
Questions


History, 02.09.2019 06:30


Spanish, 02.09.2019 06:30

Biology, 02.09.2019 06:30


Social Studies, 02.09.2019 06:30

Social Studies, 02.09.2019 06:30

History, 02.09.2019 06:30



English, 02.09.2019 06:30

Mathematics, 02.09.2019 06:30

Physics, 02.09.2019 06:30



Health, 02.09.2019 06:30



Mathematics, 02.09.2019 06:30

![-r_A=k\times\left[A\right]^\alpha\times\left[B\right]^\beta\bigm](/tpl/images/0227/4892/e6011.png)