
Chemistry, 26.11.2019 00:31 IzzybellaRamilo
The reaction 2no(g)+o2(g)−→−2no2(g) is second order in no and first order in o2. when [no]=0.040m, and [o2]=0.035m, the observed rate of disappearance of no is 9.3×10−5m/s.
(a) what is the rate of disappearance of o2 at this moment?
(b) what is the value of the rate constant?
(c) what are the units of the rate constant?
(d) what would happen to the rate if the concentration of no were increased by a factor of 1.8?

Answers: 1


Another question on Chemistry

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 02:50
What is the overall order of reaction for rate = k[no2]2 ? second order 3/2 order third order zero order none of the listed answers are correct
Answers: 3

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 07:30
Identify two types of chemical bonding in the source of dietary potassium
Answers: 3

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 16:40
Let the ed50 of a recreational drug be defined as the amount required for 50% of a test group to feel high or get a buzz. if the ed50 value of ethanol is 470 mg/kg body mass, what dose would a 70 kg party goer need to quickly consume in order to have a 50% chance of getting a buzz? 235 mg 470 mg 32,900 mg 35,000,000 mg
Answers: 3

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 19:40
What causes different colors to appear in the sky? the absorption of light by air molecules the reflection of light by bodies of water the greenhouse effect in earth's atmosphere the scattering and reflection of light by dust particles
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
The reaction 2no(g)+o2(g)−→−2no2(g) is second order in no and first order in o2. when [no]=0.040m, a...
Questions



Spanish, 15.04.2021 17:50


Geography, 15.04.2021 17:50





Mathematics, 15.04.2021 17:50


Mathematics, 15.04.2021 17:50



Social Studies, 15.04.2021 17:50


Mathematics, 15.04.2021 17:50



Mathematics, 15.04.2021 17:50

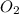 is:
is:  M/s
M/s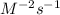
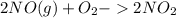
![-\frac{1}{2} \frac{d}{dt}[NO]](/tpl/images/0390/5846/9a676.png) =
= ![-\frac{d}{dt}[O_{2}]](/tpl/images/0390/5846/2117c.png) =
= ![\frac{1}{2}\frac{d}{dt}[NO_{2}]](/tpl/images/0390/5846/27827.png) -----(1)
-----(1)![[NO]^{2}[O_{2}]](/tpl/images/0390/5846/d8f06.png) -----(2)
-----(2)![-\frac{d}{dt}[NO]](/tpl/images/0390/5846/badcd.png) =
= 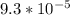 M/s.
M/s.![\frac{rate}{[NO]^{2}[O_{2}]}](/tpl/images/0390/5846/0588c.png)
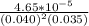 = 0.83036
= 0.83036 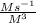 =
= ![rate\alpha [NO]^{2}](/tpl/images/0390/5846/ed652.png)
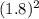 = 3.24
= 3.24

