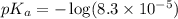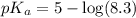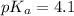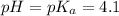The half‑equivalence point of a titration occurs half way to the equivalence point, where half of the analyte has reacted to form its conjugate, and the other half still remains unreacted. If 0.440 moles of a monoprotic weak acid ( K a = 8.3 × 10 − 5 ) is titrated with NaOH , what is the pH of the solution at the half‑equivalence point?

Answers: 2


Another question on Chemistry


Chemistry, 22.06.2019 05:50
What are the 4 phases of matter in order of increasing engery content?
Answers: 2


Chemistry, 22.06.2019 15:30
Each of the following reactions is allowed to come to equilibrium and then the volume is changed as indicated. predict the effect (shift right, shift left, or no effect) of the indicated volume change. drag the appropriate items to their respective bins.co(g) + h2o(g) < => co2(g) + h2(g) (volume is decreased) pcl3(g) + cl2(g) < => pcl5(g) (volume is increased) caco3(s)< => cao(s) + co2(g) (volume is increased)
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
The half‑equivalence point of a titration occurs half way to the equivalence point, where half of th...
Questions

Mathematics, 03.04.2021 06:40

History, 03.04.2021 06:40

Mathematics, 03.04.2021 06:40

Social Studies, 03.04.2021 06:40


Mathematics, 03.04.2021 06:40

Mathematics, 03.04.2021 06:40


Mathematics, 03.04.2021 06:40


Physics, 03.04.2021 06:40

Social Studies, 03.04.2021 06:40

World Languages, 03.04.2021 06:40

Mathematics, 03.04.2021 06:40

English, 03.04.2021 06:40


Chemistry, 03.04.2021 06:40

Biology, 03.04.2021 06:40


Mathematics, 03.04.2021 06:40

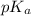 of weak acid.
of weak acid.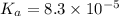
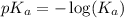
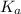 in this expression, we get:
in this expression, we get: