
Engineering, 19.07.2019 21:30 alainacorkell2087
Air with a mass flow rate of 2.3 kg/s enters a horizontal nozzle operating at steady state at 420 k, 350 kpa, and velocity of 3 m/s. at the exit, the temperature is 300 k and the velocity is 460 m/s. using the ideal gas model for air with constant ep=1.011 k/kg. k, determine: (a) the area at the inlet, in m2 (b) the heat transfer to the nozzle from its surroundings, in kw.

Answers: 1


Another question on Engineering

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:10
Afull journal bearing has a journal diameter of 27 mm, with a unilateral tolerance of -0.028 mm. the bushing bore has a diameter of 27.028 mm and a unilateral tolerance of 0.04 mm. the l/d ratio is 0.5. the load is 1.3 kn and the journal runs at 1200 rev/min. if the average viscosity is 50 mpa-s, find the minimum film thickness, the power loss, and the side flow for the minimum clearance assembly.
Answers: 1

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:10
Assuming compressible flow of air and that the measurements are done at flagstaff a pitot static tube that gives the difference of total and static pressure measures 0.35 m of mercury. what is the velocity of air? assume the temperature to be 300k. (submit your excel or matlab calculation sheet)
Answers: 1

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:10
Water at the rate of 1 kg/s is forced through a tube with a 2.5 cm inner diameter. the inlet water temperature is 15°c, and the outlet water temperature is 50°c. the tube wall temperature is 14°c higher than the local water temperature all along the length of the tube. what is the length of the tube?
Answers: 3

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:20
Prove the equivalence between the two statements of the 2nd law of thermodynamics (i.e., a violation of one statement leads to the violatio the other statement)
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
Air with a mass flow rate of 2.3 kg/s enters a horizontal nozzle operating at steady state at 420 k,...
Questions

















Computers and Technology, 21.06.2021 16:30



Health, 21.06.2021 16:30

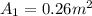
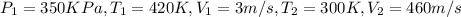
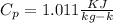
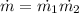
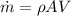
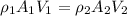
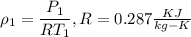
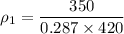
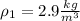
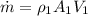
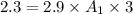
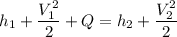
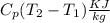
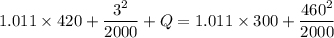
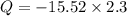 KW
KW

