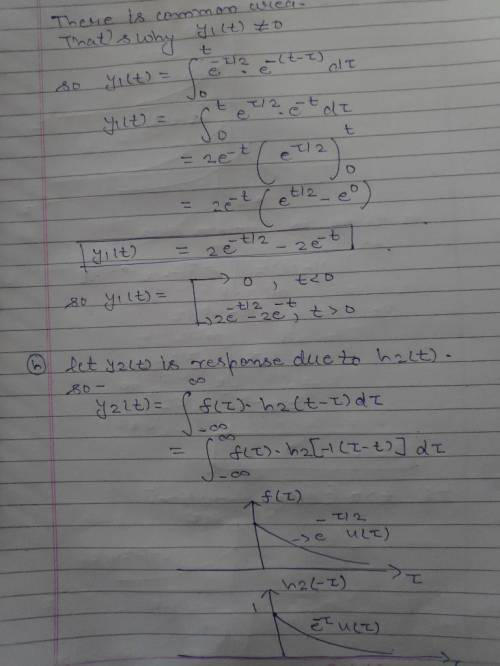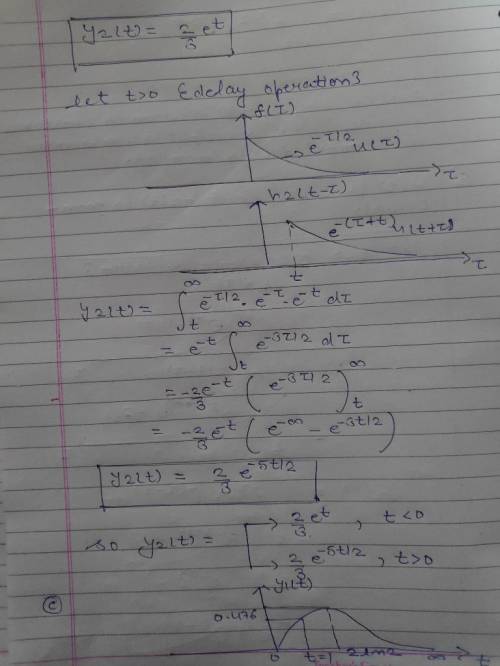Engineering, 06.03.2020 22:41 lcar61
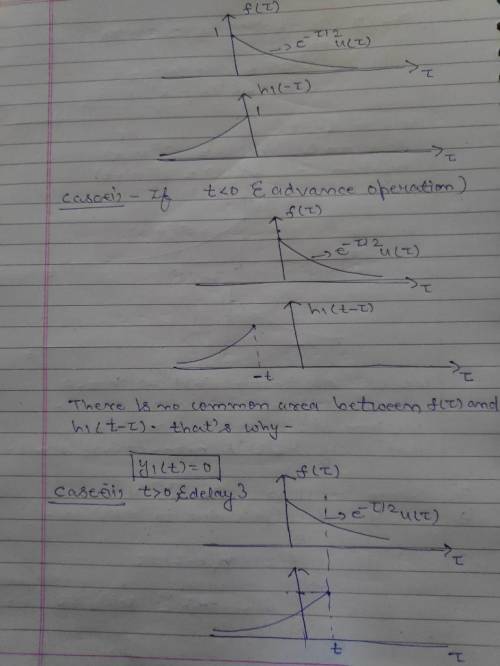
When the impulse response function h(t) is a causal signal, then the system is causal. Conversely, if the system impulse response is noncausal then the system is noncausal. To illustrate this important concept, consider two LTI systems that are represented by the impulse response functionsSystem 1: h1(t)=u(t) exp(-t)System 2: h2(t)=u(-t) exp(t)Specify whether or not the system is casual?

Answers: 1


Another question on Engineering

Engineering, 03.07.2019 14:10
Amass of 1.5 kg of air at 120 kpa and 24°c is contained in a gas-tight, frictionless piston-cylinder device. the air is now compressed to a final pressure of 720 kpa. during the process, heat is transferred from the air such that the temperature inside the cylinder remains constant. calculate the boundary work input during this process.
Answers: 2

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:10
Determine whether or not it is possible to compress air adiabatically from k to 140 kpa and 400 k. what is the entropy change during this process?
Answers: 3

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:10
Which one from below is not one of the reasons of planning failures? (clo3) a)-planner is careless. b-planner spend less time in the field but more time on the desk c)-planner is not qualified d)-planner does not have sufficient time to properly plan
Answers: 3

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:20
An engine runs on the ideal diesel cycle. the cycle has a compression ratio of 20 and a cutoff ratio of 2. the highest temperature in the cycle is 1200 k. if the heat into the system is 300 kj/kg of working fluid and using variable specific heats determine the work produced per mass of working fluid
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
When the impulse response function h(t) is a causal signal, then the system is causal. Conversely, i...
Questions

Chemistry, 12.01.2020 05:31


Mathematics, 12.01.2020 05:31



Geography, 12.01.2020 05:31

Mathematics, 12.01.2020 05:31


Business, 12.01.2020 05:31

Mathematics, 12.01.2020 05:31



Mathematics, 12.01.2020 05:31




Mathematics, 12.01.2020 05:31


Mathematics, 12.01.2020 05:31