
History, 10.10.2021 20:20 lillygon81
Until the 1760’s, people in the colonies had been making their own rules and laws. Around that time, the British had been fighting a war with France and were left with a lot of_ from the cost of the war. They felt that the colonists owed them some money from the war and that placing_ on the colonists would be a good way to raise money. King George III and the British Parliament placed many taxes on the colonists. Some of them are listed below:
• Sugar Act, 1764- placed a tax on sugar (and other goods, such as coffee, wine, and cloth) brought in from other countries
• _Act, 1765- placed a tax on legal documents, pamphlets, playing cards, licenses, newspapers, and insurance policies. When a colonist bought one of these items, a stamp was put on it to prove that the tax had been paid
• Townshend Act, 1767- placed a tax on certain items (tea, paint, lead, glass, paper) that had to be bought from Great Britain as they were not produced in the colonies
These taxes angered the colonists, especially because they were passed without their consent. A common angry cry from the colonists on this matter was: “No taxation without_. “Besides the taxes, King George and the British Parliament passed many other laws that the colonist’s thought were unfair. They did not have any representation in Parliament and therefore had no say about the passage of the laws. One way the colonists thought of to protest the taxes, was to_, or refuse to buy taxed products. In some cases, the taxes were repealed.
But they were usually replaced with other taxes.
The king was worried about the grumbling among the colonists. He decided to send an army to the colonies to control the colonists. The army was given many powers that the colonists thought was unfair and violated their rights. The Parliament continued to pass laws placing restrictions on the colonists. Some of these were:
• Response area Act, 1765- required that British soldiers be quartered (housed and fed) in
public and commercial properties at the owner’s expense.
• Declaratory Act, 1766- gave Parliament the power to pass laws (and enact taxes) on the
colonies
• _Acts, or Coercive Acts, a series of laws which:
- Allowed a colonist’s trial to be moved to another colony, or to England
- Banned all town meetings that didn’t have Royal Governor approval
- Closed Boston harbor and blockaded it with warships
- Required colonists to quarter troops in their homes if needed
The Intolerable Acts were the final straw. The colonist’s anger was growing daily. People were beginning to call for freedom and_ from Great Britain. The time that followed would see: the meeting of the _ in Philadelphia (which sent a petition for rights to the King); the formation of an army led by George Washington; and the beginning of the Revolutionary War against Great Britain. When the King did not answer the petition from the First Continental Congress, and battles started at both Lexington and Concord, it was decided that the congress should reconvene. All colonies were asked to send representatives to the_. By July of 1775, representatives from all 13 colonies had arrived, and the discussions began. At first, it was hoped that the problem could be solved peacefully, and Great Britain would change some of their rules and laws. When that did not happen, the representatives knew that the American people had had enough and that it was time to declare freedom from Great Britain and set up their own independent country.
A committee was appointed to write a statement explaining the group’s ideas on independence. Thomas Jefferson was the main writer of the statement. The final document was called the_
The Declaration had three parts:
1) The_, which explained the purpose of the Declaration
2) An outline which explained the colonists’ views and ideas about _and
3) A list of Response area, or complaints, against the king and British Parliament.
The list of grievances, though not the most important part, was the longest part of the Declaration of Independence.
Among the 27 complaints listed in this section were that the King and Parliament:
• Refused to pass laws that were good for the people
• Passed laws without the colonists’ approval
• Taxed the colonists without their approval
• Kept a British army in the colonies when there was no war
• Required the colonists to house British soldiers
• Controlled the courts
• Denied some people the right to a jury trial
On July 4, 1776, the Second Continental Congress approved the Declaration of Independence. The signers stated that as the Representatives of the United States of America, they declare that the united Colonies are free and independent, and no longer owe allegiance to the British Crown.
The words to fill the blanks are in the picture
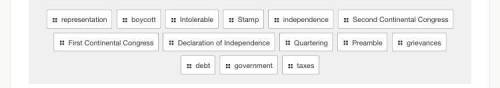

Answers: 3


Another question on History

History, 21.06.2019 14:00
Because of the conflict in the persian gulf and several attacks by iran on the u.s. fleet in the gulf, war is declared on iran. which congressional power is involved?
Answers: 1

History, 21.06.2019 15:40
Which of the following is an example of one of the successes of the marshall plan? a. a few eastern european countries decided to turn to democracy. b. western european economies were stronger than they had been before wwii. c. borders between western and eastern european countries shifted. d. eastern european countries eventually took part in the plan. ( answer in the format above so i can understand)
Answers: 2

History, 21.06.2019 19:00
How were japan's actions before and during world war 2 compare with germany's actions over the same period
Answers: 2

You know the right answer?
Until the 1760’s, people in the colonies had been making their own rules and laws. Around that time,...
Questions







Chemistry, 28.08.2019 19:10





Health, 28.08.2019 19:10




Computers and Technology, 28.08.2019 19:10


Business, 28.08.2019 19:10


Biology, 28.08.2019 19:10



