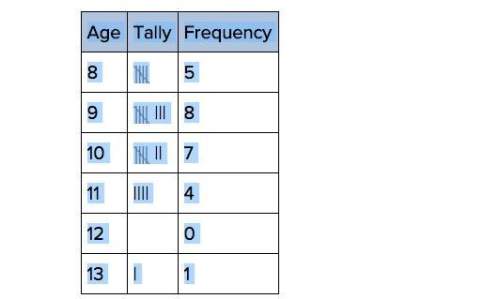
Mathematics, 29.10.2019 04:31 maliyahclays
Here is another version of the quotient-remainder theorem: given any integers n, d with dメ0, there exist unique integers q, r satisfying (1) n dq + r (2)-d/2 < r d/2 find the quotient and remainder (using the theorem above! ) for the following pairs of integers n= 11,d=2 n 11, d ,r= n=-11, d=3 q= re n= 54 d = 7 -54 d 7 qf ,r= n= 52 d-8 qf n=-52 d = 8

Answers: 3


Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 16:00
If f(x)= 3x+6 which of the following is the inverse of f(x)
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 17:00
The area of a rectangle is 54x^9y^8 square yards.if the length of the rectangle is 6x^3y^4 yards,which expression represents the width of the rectangle in yards
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 22:30
Atotal of 766 tickets were sold for the school play. they were either adult tickets or student tickets. there were 66 more student tickets sold than adult tickets. how many adult tickets were sold?
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 00:00
Answer asap! show all work! find the number of complex roots, the possible number of real roots and the possible rational roots of the polynomial function. then, solve for all roots. x^3 + 2x^2 + 3x + 6 = 0
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
Here is another version of the quotient-remainder theorem: given any integers n, d with dメ0, there...
Questions


Mathematics, 16.04.2020 17:50



Social Studies, 16.04.2020 17:50

Mathematics, 16.04.2020 17:50







Mathematics, 16.04.2020 17:51


History, 16.04.2020 17:51

Mathematics, 16.04.2020 17:51