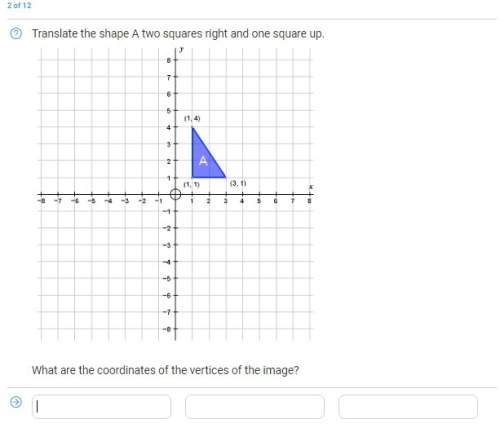
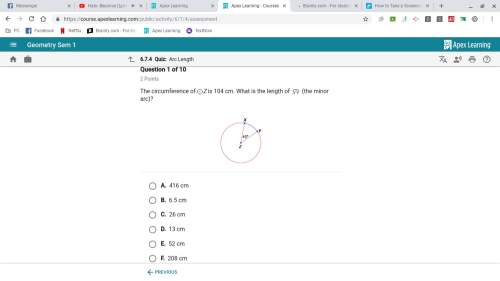
Mathematics, 25.01.2020 05:31 fantasticratz2
Dima is practicing math fluency. she has 100 math operation flashcards with 42 addition problem cards, 56 subtraction cards, and 2 multiplication cards. she will time herself to see how fast she can solve the problems on ten cards. she chooses her ten cards and they are all subtraction cards. is choosing all subtraction cards likely? explain by running a simulation.
part a: state the problem or question and assumptions.
part b: describe the process for one repetition, including possible outcomes, assigned representations, and measured variables.
part c: use digits from a table of random digits or use your calculator to perform one repetition. submit the list of random digits and indicate those that represent subtraction cards.
part d: suppose there were 17 times when all ten cards were subtraction cards after 2,000 repetitions of the simulation. state your conclusions from these results.

Answers: 2


Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 13:50
Examine the following sets of events. set a: {1, 5, 7, 9, 14} set b: {2, 5, 6, 8, 14, 17} which of the following represents the intersection of set a and set b ? {∅} {5, 14} {1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 14, 17} {1, 2, 6, 7, 8, 9, 17}
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 15:00
Need ! give step by step solutions on how to solve number one \frac{9-2\sqrt{3} }{12+\sqrt{3} } number two x+4=\sqrt{13x-20} number three (domain and range) f(x)=2\sqrt[3]{x} +1
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 17:00
In tossing one coin 10 times, what are your chances for tossing a head? a tail? 2. in tossing one coin 100 times, what are your chances for tossing a head? a tail? 3. in tossing one coin 200 times, what are your chances for tossing a head? a tail? deviation = ((absolute value of the difference between expected heads and observed heads) + (absolute value of the difference between expected tails and observed tails)) divided by total number of tosses. this value should always be positive. 4. what is the deviation for 10 tosses? 5. what is the deviation for the 100 tosses? 6. what is the deviation for 200 tosses? 7. how does increasing the total number of coin tosses from 10 to 100 affect the deviation? 8. how does increasing the total number of tosses from 100 to 200 affect the deviation? 9. what two important probability principles were established in this exercise? 10. the percent of occurrence is the obtained results divided by the total tosses and multiplied by 100%. toss the coins 100 times and record your results. calculate the percent occurrence for each combination. percent head-head occurrence: percent tail-tail occurrence: percent head-tail occurrence:
Answers: 3

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 20:00
Find the value of x. round the length to the nearest tenth
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
Dima is practicing math fluency. she has 100 math operation flashcards with 42 addition problem card...
Questions

Chemistry, 28.01.2021 23:30


Biology, 28.01.2021 23:30




Biology, 28.01.2021 23:30



Mathematics, 28.01.2021 23:30



Mathematics, 28.01.2021 23:30

Mathematics, 28.01.2021 23:30


Physics, 28.01.2021 23:40



Social Studies, 28.01.2021 23:40