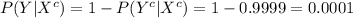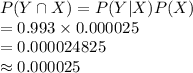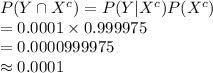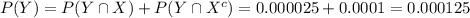Mathematics, 28.02.2020 19:19 vspink9962
The sensitivity is about 0.993. That is, if someone has HIV, there is a probability of 0.993 that they will test positive. • The specificity is about 0.9999. This means that if someone doesn’t have HIV, there is probability of 0.9999 that they will test negative. In the general population, incidence of HIV is reasonably rare. It is estimated that the chance that a randomly chosen person has HIV is 0.000025. To investigate the possibility of implementing a random HIV-testing policy with the Elisa test, calculate the following: a. The probability that someone will test positive and have HIV. b. The probability that someone will test positive and not have HIV. c. The probability that someone will test positive. d. Suppose someone tests positive. What is the probability that they have HIV? In light of the last calculation, do you envision any problems in implementing a random testing policy?

Answers: 1


Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 23:30
Identify the slope an intercept of the following linear equation y = 1/5x - 6 a. slope: 1/5; intercept: -6 b. slope: 5; intercept: -6 c. slope: -1/5; intercept: 6 d. slope: 1/5; intercept: 6
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 23:40
Find the amplitude of a sinusoidal function that models this temperature variation
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 03:00
The sum of four times a number and three is two times the number minus twenty nine
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 03:00
The triangle rst, rs = 65 and st = 60. which equation could be used to find the value of angle s?
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
The sensitivity is about 0.993. That is, if someone has HIV, there is a probability of 0.993 that th...
Questions

Mathematics, 19.02.2020 15:55



Health, 19.02.2020 15:57

History, 19.02.2020 15:57


Physics, 19.02.2020 15:58

History, 19.02.2020 15:59


English, 19.02.2020 16:00

Physics, 19.02.2020 16:00


Mathematics, 19.02.2020 16:01

Mathematics, 19.02.2020 16:01


Advanced Placement (AP), 19.02.2020 16:03

Mathematics, 19.02.2020 16:06

Mathematics, 19.02.2020 16:07

Mathematics, 19.02.2020 16:08

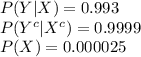
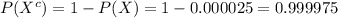
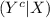 as follows:
as follows: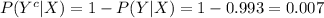
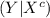 follows:
follows: