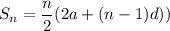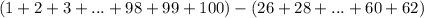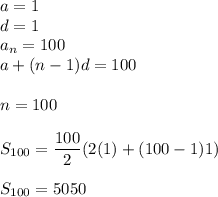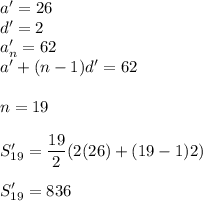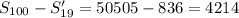Mathematics, 02.03.2020 16:50 keva1p6dk26
The sum S of the arithmetic sequence a, a + d, a + 2d, . . . , a + (n – 1)d is given by \small S=\frac{n}{2}\left [2a+(n-1)d \right ] . What is the sum of the integers from 1 to 100, inclusive, with the even integers between 25 and 63 omitted?

Answers: 3


Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 20:00
Evaluate the discriminant of each equation. tell how many solutions each equation has and whether the solutions are real or imaginary. x^2 + 4x + 5 = 0
Answers: 2


Mathematics, 22.06.2019 00:30
Long division setup showing an incomplete calculation. 12 is in the divisor, 6839 is in the dividend, and 5 hundreds and 6 tens is written in the quotient. 6000 is subtracted from 6839 to give 839. an unknown value represented by a box is being subtracted from 839. what number should be placed in the box to complete the division calculation?
Answers: 3

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 00:30
Given abc find the values of x and y. in your final answer, include all of your calculations.
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
The sum S of the arithmetic sequence a, a + d, a + 2d, . . . , a + (n – 1)d is given by \small S=\fr...
Questions






Health, 20.11.2020 22:20

Mathematics, 20.11.2020 22:20

Mathematics, 20.11.2020 22:20

Mathematics, 20.11.2020 22:20



Mathematics, 20.11.2020 22:20



Advanced Placement (AP), 20.11.2020 22:20

English, 20.11.2020 22:20

English, 20.11.2020 22:20

Advanced Placement (AP), 20.11.2020 22:20