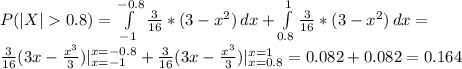Mathematics, 30.03.2020 21:35 ashleymunoz928
3.30 Measurements of scientific systems are always subject to variation, some more than others. There are many structures for measurement error, and statisticians spend a great deal of time modeling these errors. Suppose the measurement error X of a certain physical quantity is decided by the density function f(x) = k(3 − x2), −1 ≤ x ≤ 1, 0, elsewhere. (a) Determine k that renders f(x) a valid density function. (b) Find the probability that a random error in measurement is less than 1/2. (c) For this particular measurement, it is undesirable if the magnitude of the error (i. e., |x|) exceeds 0.8. What is the probability that this occurs?

Answers: 3


Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 16:00
Which term best describes the association between variables a and b? no association a negative linear association a positive linear association a nonlinear association a scatterplot with an x axis labeled, variable a from zero to ten in increments of two and the y axis labeled, variable b from zero to one hundred forty in increments of twenty with fifteen points in a positive trend.
Answers: 2


Mathematics, 21.06.2019 19:30
Acar started driving from city a to city b, distance between which is 620 miles, at a rate of 60 mph. two hours later a truck left city b and started moving towards city a at a rate of 40 mph. how many hours after the truck's departure will the two meet?
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 23:00
Astore sells 4 apples for $3 and 3 oranges for $4 if pete buys 12 apples and 12 oranges how much will it cost
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
3.30 Measurements of scientific systems are always subject to variation, some more than others. Ther...
Questions

Social Studies, 21.04.2020 16:11




Mathematics, 21.04.2020 16:11


Mathematics, 21.04.2020 16:12










English, 21.04.2020 16:12

History, 21.04.2020 16:12

Mathematics, 21.04.2020 16:12

![1 = k \int\limits^1_{-1} {(3-x^2)} \, dx = k * (3x-\frac{x^3}{3})|_{x=-1}^{x = 1} = k*[(3-1/3) - (-3 + 1/3)] = 16k/3](/tpl/images/0571/3484/7e564.png)
![P(X < 1/2) = \int\limits^{0.5}_{-1} {\frac{3}{16}(3-x^2)} \, dx = \frac{3}{16} [(3x-\frac{x^3}{3}) |_{x=-1}^{x=0.5}] =\frac{3}{16} *(1.458333 - (-3+1/3)) = 0.7734](/tpl/images/0571/3484/211f5.png)