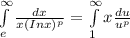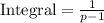Mathematics, 07.06.2020 04:01 igtguith
Find the values of p for which the following integral converges:
∫[infinity]e 1/(x(ln(x))^p)dx
Input youranswer by writing it as an interval. Enter brackets or parentheses in the first and fourth blanks as appropriate, and enter the interval endpoints in the second and third blanks. Use INF and NINF (in upper-case letters) for positive and negative infinity if needed. If the improper integral diverges for all p, type an upper-case "D" in every blank.
Values of p are in the interval ,
For the values of p at which the integral converges, evaluate it. Integral =

Answers: 1


Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 16:30
Acircle has a circumference of 2 pi cm. which statement about the circumference and area is true? a comparison of the area and circumference is not possible since the area cannot be determined. the numerical values of the circumference and area of the circle are equal. the numerical value of the circumference is greater than the numerical value of the area. the numerical value of the circumference is less than the numerical value of the area.
Answers: 3

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 17:30
Adozen bananas weigh 3 pounds how many ounces does 1 banana weigh
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 18:50
The table represents a function f(x). what is f(3)? a.-9 b.-1 c.1 d.9
Answers: 1

You know the right answer?
Find the values of p for which the following integral converges:
∫[infinity]e 1/(x(ln(x))^p)dx
Questions

Mathematics, 14.06.2020 05:57


Mathematics, 14.06.2020 05:57












Mathematics, 14.06.2020 05:57

Chemistry, 14.06.2020 05:57




Mathematics, 14.06.2020 05:57

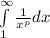
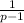 and divertgent if p ≤ 1
and divertgent if p ≤ 1