
Physics, 09.09.2019 17:30 sshaynijaonnahayde
In the theory of relativity, the mass of a particle with velocity v is  , where m₀ is the mass of the particle at rest and c is the speed of light. what happens as v → c⁻?
, where m₀ is the mass of the particle at rest and c is the speed of light. what happens as v → c⁻?
a. m → m₀
b. m → 1
c. m → 0
d. m → m⁻

Answers: 3


Another question on Physics

Physics, 21.06.2019 21:30
According to social exchange theory, altruistic behaviors benefit the individual who performs them. t/f
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 06:00
The magnetic field inside a superconducting solenoid is 4.50 t. the solenoid has an inner diameter of 6.20 cm and a length of 26.0 cm. determine (a) the magnetic energy density in the field and (b) the energy stored in the magnetic field within the solenoid.
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 11:30
Which accounts for an increase in the temperature of a gas that is kept a constant volume
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 12:00
The sun’s mass is 2.0×10^ 30 kg, its radius is 7.0×10 5 km, and it has a rotational period of approximately 28 days. if the sun should collapse into a white dwarf of radius 3.5×10 3 km, what would its period be if no mass were ejected and a sphere of uniform density can model the sun both before and after?
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
In the theory of relativity, the mass of a particle with velocity v is [tex]m = \frac{m_0}{\sqrt{1 -...
Questions

Social Studies, 28.11.2020 16:50

Mathematics, 28.11.2020 16:50

Business, 28.11.2020 16:50

English, 28.11.2020 16:50

Biology, 28.11.2020 16:50

World Languages, 28.11.2020 16:50


Mathematics, 28.11.2020 16:50





Mathematics, 28.11.2020 17:00



History, 28.11.2020 17:00

Mathematics, 28.11.2020 17:00

Social Studies, 28.11.2020 17:00


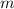 would tend to infinite.
would tend to infinite.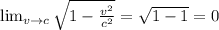
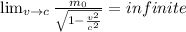 .
. . It also means that a particle would need infinite energy to travel at light speed.
. It also means that a particle would need infinite energy to travel at light speed.

