
Physics, 13.04.2020 18:16 calebabaltimore
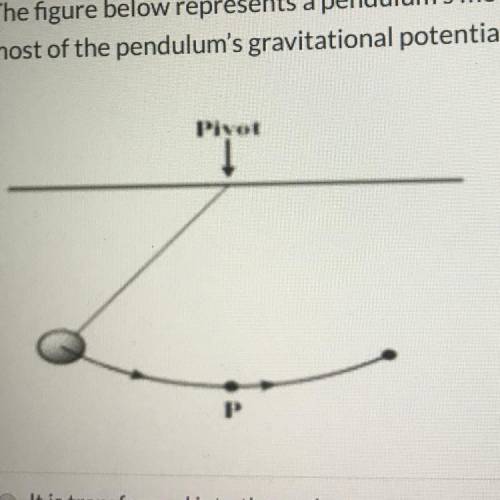
The figure below represents a pendulum's motion with the lowest point of its swing labeled P. What happens to
most of the pendulum's gravitational potential energy as it reaches the lowest point P?
(picture inserted)
a. It is transformed into thermal energy.
b. It is transformed into inertia.
c. It is transformed into chemical energy
d. It is transformed into kinetic energy.

Answers: 2


Another question on Physics

Physics, 21.06.2019 23:20
Imagine you had to physically add electrons, one at a time, to a previously neutral conductor. you add one electron very easily, but the second electron requires more work. in your initial post to the discussion, explain why this is. also, what happens to the work needed to add the third, fourth, fifth, and subsequent electrons
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 11:00
Consider a system to be two train cars traveling toward each other. what is the total momentum of the system before the train cars collide? kg • what must the total momentum of the system be after the train cars collide? kg •
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 12:30
Consider a hydrogen atom in the ground state. what is the energy of its electron? =e= jj now consider an excited‑state hydrogen atom. what is the energy of the electron in the =5n=5 level? =e5= j
Answers: 3

Physics, 22.06.2019 23:00
Acommon technique in analysis of scientific data is normalization. the purpose of normalizing data is to eliminate irrelevant constants that can obscure the salient features of the data. the goal of this experiment is to test the hypothesis that the flux of light decreases as the square of the distance from the source. in this case, the absolute value of the voltage measured by the photometer is irrelevant; only the relative value conveys useful information. suppose that in part 2.2.2 of the experiment, students obtain a signal value of 162 mv at a distance of 4 cm and a value of 86 mv at a distance of 5.7 cm. normalize the students' data to the value obtained at 4 cm. (divide the signal value by 162.) then calculate the theoretically expected (normalized) value at 5.7 cm.
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
The figure below represents a pendulum's motion with the lowest point of its swing labeled P. What h...
Questions


Biology, 10.07.2019 13:00







Arts, 10.07.2019 13:00


Chemistry, 10.07.2019 13:00

Mathematics, 10.07.2019 13:00

Mathematics, 10.07.2019 13:00


Biology, 10.07.2019 13:00


English, 10.07.2019 13:00

Biology, 10.07.2019 13:00


Social Studies, 10.07.2019 13:00



