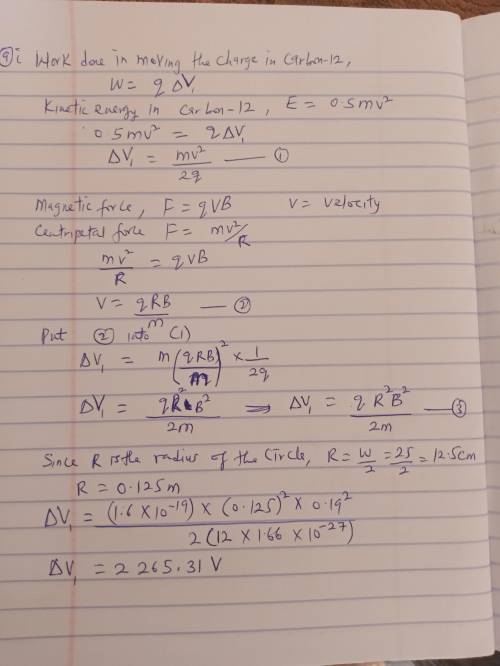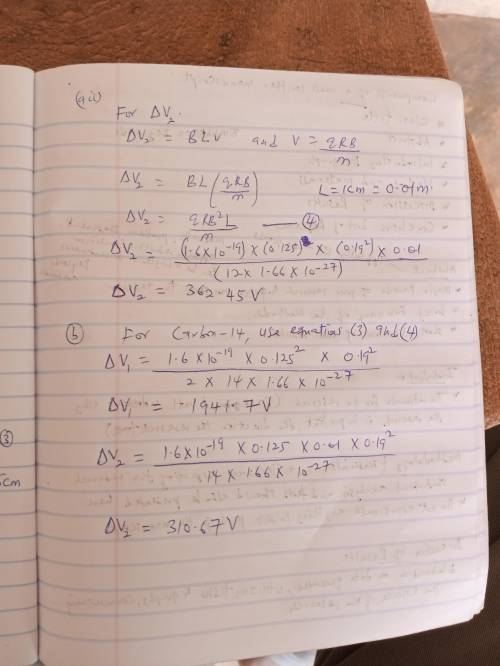Physics, 05.05.2020 03:43 kaylaaguilar6538
Mass spectrometer A mass spectrometer is a tool used to determine accurately the mass of individual ionized atoms or molecules, or to separate atoms or molecules that have similar but slightly different masses. For example, you can deduce the age of a small sample of cloth from an ancient tomb, by using a mass spectrometer to determine the relative abundances of carbon-14 (whose nucleus contains 6 protons and 8 neutrons) and carbon-12 (the most common isotope, whose nucleus contains 6 protons and 6 neutrons). In organic material, the ratio of 14C to 12C depends on how old the material is, which is the basis for "carbon-14 dating." 14C is continually produced in the upper atmosphere by nuclear reactions caused by "cosmic rays" (high-energy charged particles from outer space, mainly protons), and 14C is radioactive with a half-life of 5700 years. When a cotton plant is growing, some of the CO2 it extracts from the air to build tissue contains 14C which has diffused down from the upper atmosphere. But after the cotton has been harvested there is no further intake of 14C from the air, and the cosmic rays that create 14C in the upper atmosphere can't penetrate the atmosphere and reach the cloth. So the amount of 14C in cotton cloth continually decreases with time, while the amount of non-radioactive 12C remains constant.
Carbon from the sample is ionized in the ion source at the left. The resulting singly ionized 12C+ and 14C+ ions have negligibly small initial velocities (and can be considered to be at rest). They are accelerated through the potential difference ΔV1. They then enter a region where the magnetic field has a fixed magnitude B = 0.19 T. The ions pass through electric deflection plates that are 1 cm apart and have a potential difference ΔV2 that is adjusted so that the electric deflection and the magnetic deflection cancel each other for a particular isotope: one isotope goes straight through, and the other isotope is deflected and misses the entrance to the next section of the spectrometer. The distance from the entrance to the fixed ion detector is a distance of w = 25 cm. There are controls that let you vary the accelerating potential ΔV1 and the deflection potential ΔV2 in order that only 12C+ or 14C+ ions go all the way through the system and reach the detector. You count each kind of ion for fixed times and thus determine the relative abundances. The various deflections ensure that you count only the desired type of ion for a particular setting of the two voltages.
Determine the appropriate numerical values of ΔV1 and ΔV2 for 12C. Carry out your intermediate calculations algebraically, so that you can use the algebraic results in the next part.
ΔV1 = 4 V
ΔV2 = 5 V
Determine the appropriate numerical values of ΔV1 and ΔV2 for 14C.
ΔV1 = 6 V
ΔV2 = 7 V

Answers: 2


Another question on Physics

Physics, 21.06.2019 16:00
28. a stone is projected at a cliff of height h with an initial speed of 42.0 mls directed at angle θ0 = 60.0° above the horizontal. the stone strikes at a, 5.50 s after launching. find (a) the height h of the cliff, (b) the speed of the stone just before impact at a, and (c) the maximum height h reached above the grou
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 03:00
Which boundary is associated with the building of the himalaya mountains? convergent transform divergent hot spot
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 05:50
High schoolphysics 5+3 pts a neon light consists of a glass tube with metal wires at each end. when connected to a high-voltage source, the gas glows. if a fly lands on the glass tube, what will most likely happen? a) the fly will not feel a shock because the glass conducts any free electrons back into the gas. b) electrons will flow directly from the metal wires along the glass and shock the fly. c) the fly will not feel a shock because the glass insulates it from the electrons in the gas and the metal. d) electrons that are moving through the gas will be conducted through the glass and shock the fly.
Answers: 3

Physics, 22.06.2019 14:10
Your starship, the aimless wanderer, lands on the mysterious planet mongo. as chief scientist-engineer, you make the following measurements: a 2.50-kg stone thrown upward from the ground at 14.0 m/s returns to the ground in 5.70 s ; the circumference of mongo at the equator is 2.20×10^5 km ; and there is no appreciable atmosphere on mongo. (a) the starship commander, captain confusion, asks for the following information: what is the mass of mongo? (b) if the aimless wanderer goes into a circular orbit 2.20×10^4 km above the surface of mongo, how many hours will it take the ship to complete one orbit? (c) an unmanned spacecraft is in a circular orbit around the moon, observing the lunar surface from an altitude of 44.0 km . to the dismay of scientists on earth, an electrical fault causes an on-board thruster to fire, decreasing the speed of the spacecraft by 23.0 m/s . if nothing is done to correct its orbit, with what speed (in km/h) will the spacecraft crash into the lunar surface?
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
Mass spectrometer A mass spectrometer is a tool used to determine accurately the mass of individual...
Questions

Mathematics, 30.01.2020 16:59


Geography, 30.01.2020 16:59


English, 30.01.2020 16:59

History, 30.01.2020 16:59

Business, 30.01.2020 16:59

Mathematics, 30.01.2020 16:59

Mathematics, 30.01.2020 16:59






Business, 30.01.2020 16:59



Mathematics, 30.01.2020 16:59