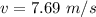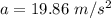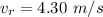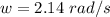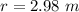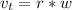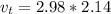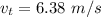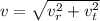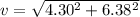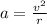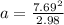Physics, 22.10.2020 19:01 tajanaewilliams77
A particle is moving in a plane with constant radial velocity \dot{r} = 4.30~\mathrm{m/s} r ˙ =4.30 m/s, having started at the origin. It also has a constant angular velocity \dot{\theta} = 2.14~\mathrm{rad/s} θ ˙ =2.14 rad/s. When the particle is 2.98~\mathrm{m}2.98 m from the origin, what is the magnitude of its acceleration in \mathrm{m/s^2}m/s 2 ?

Answers: 1


Another question on Physics

Physics, 22.06.2019 17:30
Alarge cruise ship of mass 7.00 ✕ 107 kg has a speed of 11.6 m/s at some instant. (a) what is the ship's kinetic energy at this time? (b) how much work is required to stop it? (give the work done on the ship. include the sign of the value in your answer.) (c) what is the magnitude of the constant force required to stop it as it undergoes a displacement of 3.00 km?
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 21:30
Which of the following best describes the circuit shown below?
Answers: 3

Physics, 23.06.2019 00:00
Boiling water is an example of physical change. true or false
Answers: 2

Physics, 23.06.2019 01:30
Aplane's average speed between two cities is 600 km/h. if the trip takes 2.5 hours, how far does the plane fly?
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
A particle is moving in a plane with constant radial velocity \dot{r} = 4.30~\mathrm{m/s} r ˙ =4.30...
Questions






Spanish, 25.08.2021 23:50


Mathematics, 25.08.2021 23:50



Mathematics, 25.08.2021 23:50

Spanish, 25.08.2021 23:50

Mathematics, 25.08.2021 23:50



Mathematics, 25.08.2021 23:50


Mathematics, 25.08.2021 23:50


Mathematics, 25.08.2021 23:50